![[PukiWiki] [PukiWiki]](image/pukiwiki.png)
![[PukiWiki] [PukiWiki]](image/pukiwiki.png)
目次
覚えておくと良いこと
ファイル保存 [Ctrl + S]
全てを保存 [Ctrl + Shift + S]
文字列検索 [Ctrl + F]
コピー[Ctrl + C] ペースト [Ctrl + V]
候補[Ctrl + Space]
Error starting ApplicationContext. To display the conditions report re-run your application with 'debug' enabled. 2021-08-20 09:26:47.234 ERROR 13740 --- [ restartedMain] o.s.b.d.LoggingFailureAnalysisReporter : *************************** APPLICATION FAILED TO START *************************** Description: Failed to configure a DataSource: 'url' attribute is not specified and no embedded datasource could be configured. Reason: Failed to determine a suitable driver class Action: Consider the following: If you want an embedded database (H2, HSQL or Derby), please put it on the classpath. If you have database settings to be loaded from a particular profile you may need to activate it (no profiles are currently active).
上記のようなエラーはデータベースのアクセスに失敗しているので
spring.datasource.url=jdbc:mysql://localhost/接続したいデータベース名 spring.datasource.username=root spring.datasource.password=MySQLのパスワード spring.datasource.driver-class-name=com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
プロジェクトファイルからresouleseの直下にapplication.propertiesあるので上記のように設定すると解決できます。
There was an unexpected error (type=Not Found, status=404). No message available
上記のようなエラーはURLが違う可能性があります。なのでコントローラークラスにあるMappingの部分を確認してください。
There was an unexpected error (type=Method Not Allowed, status=405). Request method 'GET' not supported org.springframework.web.HttpRequestMethodNotSupportedException: Request method 'GET' not supported
上記のようなエラーはコントローラークラスのMappingのGetとPostが正しいか確認してください。
There was an unexpected error (type=Internal Server Error, status=500). An error happened during template parsing (template: "class path resource [templates/testpage.html]")
上記のようなエラーが出たら画面を下にスクロールしていくと下記の通りにhtmlファイルの何行目にエラーがあるか分かります。
Caused by: org.attoparser.ParseException: Could not parse as expression: "/create/view" (template: "testpage" - line 10, col 4)
記述にミスがあると思うのでリファレンスなど調べて修正してください。
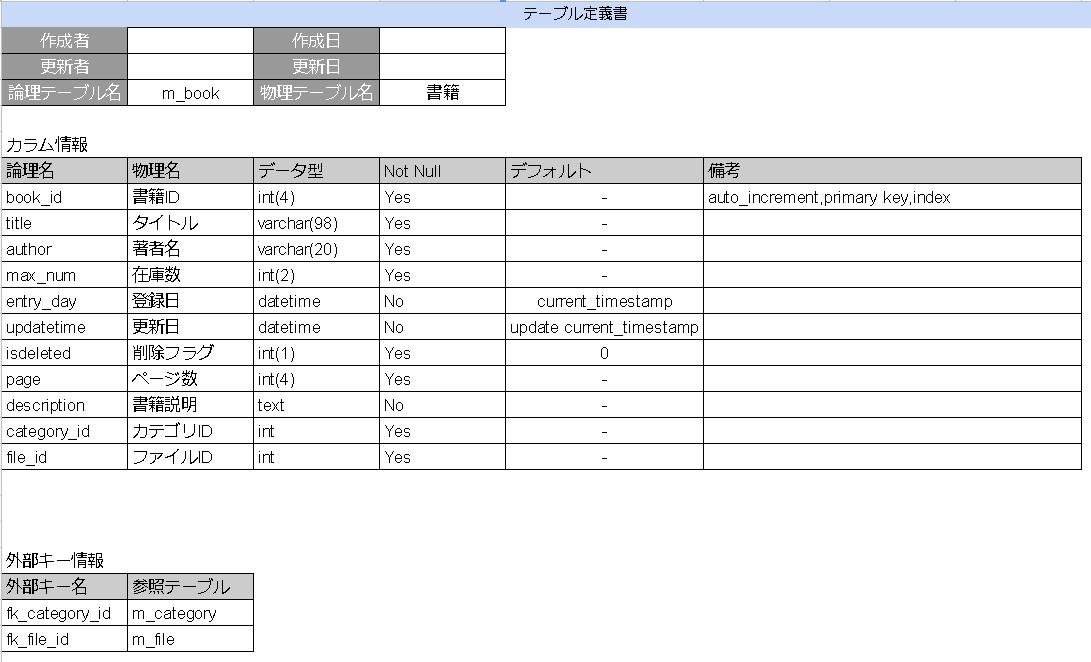
テーブル定義書とはテーブルを作成するための設計書です。データベースにテーブルを定義するためのDDL文を作成するために必要な設計書ということです。
| 画面 | 区分1 | 区分2 | 確認項目 | 結果 |
| ログイン | テキストボックス | メールアドレス | 文字が入力できること 必須項目になっていること | OK |
| パスワード | 文字が入力できること 必須項目になっていること 入力したときに***で隠れていること | NG |
多重度はそのクラスのインスタンスが何個関連を持つかを表します。表記法としては以下の3パターンを覚えておけば十分でしょう。n..m:n以上m以下n..*:n以上n , m:n個またはm個
Visual Studio Codeを開きます。
左側のメニューに拡張機能があるので
PlantUMLと入力してください
検索すると一番上に出てくると思うのでクリックしてインストールします。
インストールが終えたら
左上のメニューにあるファイルから新規作成を選択してください。
Untitled-1が作成されるのでCTRL + SHIFT + S を押します。
任意のファイル名を入力し、ファイルの種類をPlantUMLに選択して保存します。
.wsdという形式のファイルができればOKです。
下記がUMLのサンプルになります。
@startuml Update mainframe ユーザー編集 actor User participant "ユーザー一覧画面" as View participant "編集モーダル" as Modal participant "エンコード" as encode participant "更新処理" as Update database "データベース" as DB alt 権限あり User -> View : 編集したい activate View else 権限なし User <-- View : エラー end View -> Modal : 一覧から選択する activate Modal Modal <-- DB : ユーザーID,変更前の名前,メールアドレス,パスワード activate DB Modal -> Update : 入力(名前,メールアドレス) activate Update Modal -> encode : 入力(パスワード) deactivate Modal activate encode encode -> Update : 暗号化したパスワード deactivate encode Update -> DB :更新 deactivate Update View <-- DB : 更新したユーザー情報を反映 deactivate DB deactivate View @enduml
ALT+Dを押すとプレビューに図が表示されます。
図を画像ファイルとして保存したい場合は
ファイル内で右クリックすると
ファイル内のダイアグラムをエクスポートとあるのでクリックします。
pngを選択するとのファイルを作成した場所にフォルダが作成されているのでフォルダ内に画像ファイルがあります。
Git Hubのアカウント作成
以下のリンクから作成してください
アカウント作成
ユーザー名とメールアドレスとパスワードを入力して登録します。
無料版であるfreeを選択してContinue押して作成されます。
Git Bashのダウンロード~インストールまで
下記からサイトへ移動してDownloadボタンを押します。
Git Bashのダウンロード
インストーラーを起動してセットアップをおこないます。
最初のウィンドウからNextを押して進みます。
Git Bash Hereにチェックが付いていることを確認して
Next
Use Git from the Windows Command Promptを選択して
Next
Use the OpenSSL libraryを選択して
Next
Checkout Windows-style,commit Unix-style line endingsを選択して
Next
Use MinTTY(the default terminal of MSYS2)を選択して
Next
Enable file system cachingとEnable Git Credential Managerにチェックを入れて
Next
いくつかチェックボックスがありますが入れずにNextを押してインストールが開始されます。
Git Bashを開いて以下のコマンドを入力してユーザーの設定をします。
git config --global user.name git config --global user.email
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
作成したxmlファイルにmybatisを使うための設定をします。
<!DOCTYPE mapper PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN" "http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd">
Mapperを指定します。
<mapper namespace="com.example.demo.mapper.UserMapper">
検索結果をデータ型に変換するためクラスをresultTypeで指定する
<select id="findUser" resultType="com.example.demo.entity.User">
select user_id,user_name from m_user;
</select>
</mapper>
parameterTypeはinsert文でvalueの値やupdateでsetする値を指定するときに使う。
こちらのサイト参考にだいたい覚えました。
@RequestParam? URLに含まれるクエリパラメータを受け取ることができる
@Autowired 外部から呼び出して自動的に初期化してくれる。
@PathVariable? @GetMapping?で指定したメソッドの引数につけると、URLに含まれる動的なパラメータを受け取ることができます。
@ModelAttribute? コントローラーの引数につけて使う HTMLのフィールド属性から値を取得することができる
@Data クラスに@Getter、@Setter、@RequiredArgsConstructor?、@EqualsAndHashCode?、@ToString?を指定したことと同じ作用になります。
@Mapper Mapperを定義するために必要なアノテーション 定義する場所はインターフェースです。
@Controller MVCパターンのCの役割を担うコンポーネント。このアノテーションを付与したコンポーネントでは、クライアントからのリクエスト/レスポンスに関わる処理をする。
@Service ビジネスロジックを実装するコンポーネントであることを表すアノテーション。
@Repository データの永続化に関わる処理を提供するコンポーネント。ORMなどを利用して、データのCRUD処理を実装する。
@Component 上記3つに当てはまらないコンポーネント。ユーティリティクラスなどに付与する。
@Configuration クラス宣言の前に記述します。このアノテーションは、このクラスがBeanの設定を行うものであることを示します。Bean設定クラスには常にこれをつけます。
Controllerクラスに書かれている@〇〇Mappingとは
簡単に言うとSpringBoot?の外部からのアクションに対するプログラムの処理の入り口です。
@RequestMapping?は全体の処理 使い方はクラスの頭に付ける
※クラス内での@RequestMapping?は避けたい@GetMapping?も@PostMapping?両方できてしまうため読んでいてわかりづらい
@GetMapping?は取得の処理 登録しているデータを取得したりします。
@PostMapping?は投稿の処理 新しいデータを登録したりします。
base64形式のメリット
base64処理を用いるメリットとしては、画像ファイルをbase64に変換すると文字列になりますので、サーバーにデータを送信する場合などに元のバイナリデータのままよりも、処理が単純になります。
また、base64エンコードされた画像はウェブページに直接埋め込むこともできます。
application.propertiesの設定
max-file-size...................................1ファイルにおける最大バイト数
max-request-size ...............................(複数アップロード時の)1リクエストにおける最大バイト数
spring.servlet.multipart.max-file-size=10MB spring.servlet.multipart.max-request-size=30MB
「org.springframework.web.multipart.multipartfile」というインタフェースでアップロードしたファイルを受け取る。
import org.springframework.web.multipart.MultipartFile;
import lombok.Data;
@Data
public class File {
private byte[] fileName;
private MultipartFile uploadFile;
}
HTML フォームの設定 「enctype="multipart/form-data"」を忘れないようにする。これを設定しないと(HTML仕様上)ファイルの中身が送信されない。
<form th:action="@{/upload}" method="post" enctype="multipart/form-data">
HTMLから受け取ったファイルの処理 controller データベースに追加するときはbyte[]の変数からBLOB型のカラムへ格納
import java.io.IOException;
import java.nio.charset.Charset;
import java.nio.charset.StandardCharsets;
import java.nio.file.Files;
import java.nio.file.Path;
import java.nio.file.Paths;
import java.security.NoSuchAlgorithmException;
import java.util.Base64;
// htmlからファイル名を受け取る 今回はjava.png
String fileName = uploadFile.getImage().getOriginalFilename();
// 受け取ったファイル名(String)からbute[]に変換し、ファイルの形式をpngからBase64形式に変換
Charset charset = StandardCharsets.UTF_8;
byte[] encode = Base64.getEncoder().encode(fileName.getBytes(charset));
// フォルダを作成する場所を指定 ※パスは各自変更
Path path = Paths.get("");
// ファイルの転送先 + ファイル
Path transferTarget = Paths.get("" + addFileName);
try{
// 転送するフォルダの作成
Files.createDirectory(path);
// メソッドを呼び出して転送する
uploadFile.getImage().transferTo(transferTarget);
}catch(IOException e){
System.out.println(e);
}
画面に出力させる処理 controller
// データベースからファイルを受け取る byte[] b = encodeFile.getFile_name(); // Base64形式から元の形式に(.png)に戻す byte[] decode = Base64.getDecoder().decode(b); // byte[]から元の文字に戻す(java.png) Charset charset = StandardCharsets.UTF_8; String strDecode = new String(decode,charset);
HTMLで保存してあるフォルダを指定して画像を表示させる
<img th:src = "'/images/'+${decodefile}">
HTML5などのテンプレートエンジン
メリットとしては変数の部分を属性値で記述しているため、ブラウザで表示しても崩れないのが大きい
使い方はこちらを参考に
この機能はJava Scriptを使って実現させます。
/**
* 返却期限の表示処理の内容
* 期限が過ぎた書籍の返却期限は赤色で表示します。
* 期限が過ぎていない書籍は黄色で表示します。
*/
// ページ読み込み時に実行処理
window.onload = function()
{
const elements = document.getElementsByClassName('class');
//現在の日付を取得します
let now_date = new Date();
let comparison_date = now_date.getFullYear() + "/" + (now_date.getMonth() + 1) + "/" + (now_date.getDate() - 2);
/* 関数の引数に書籍の返却予定日と書籍ID
HTMLのname属性には返却予定日を格納してid属性には書籍IDを格納しています*/
function comparison(name, id)
{
// 返却期限が過ぎている時
if (new Date(comparison_date) > new Date(name))
{
let book_object = document.getElementById(id);
book_object.style.backgroundColor = '#ff2020';
}
// 返却期限が過ぎていない時
else
{
let book_object = document.getElementById(id);
book_object.style.backgroundColor = '#fff450';
}
}
// 借りている書籍の数だけ処理をする
for (let step = 0; step < elements.length; step++)
{
comparison(elements[step].name, elements[step].id);
}
}
jQueryを使った作成方法
HTMLはこんな感じです。
<link rel="stylesheet" href="/css/****.css"> <script src="https://ajax.googleapis.com/ajax/libs/jquery/2.1.4/jquery.min.js"></script> <script src="/js/****.js"></script> <button type = "button" class = "modal-button"></button> <div id="modal-content"> <p>モーダルウィンドウに表示されます。</p> </div>
CSSにはオーバーレイとモーダルの設定を書きます。
#modal-content {
width: 50% ;
height: 50% ;
margin: 0 ;
padding: 10px 20px ;
border: 2px solid #aaa ;
background: #fff ;
position: fixed ;
display: none ;
z-index: 2 ;
}
#modal-overlay {
z-index: 1 ;
display: none ;
position: fixed ;
top: 0 ;
left: 0 ;
width: 100% ;
height: 120% ;
background-color: rgba( 0,0,0, 0.75 ) ;
}
jQueryにはオーバレイとモーダルの操作を書きます。
$(function() {
$('.modal-button').click(function() {
/*キーボード操作などにより、オーバーレイが多重起動するのを防止する
ボタンからフォーカスを外す*/
$(this).blur();
//新しくモーダルウィンドウを起動しない
if ($("#modal-overlay")[0]) return false;
//オーバーレイを出現させる
$("body").append('<div id="modal-overlay"></div>');
$("#modal-overlay").fadeIn("slow");
//モーダルウィンドウをセンタリングする
centeringModalSyncer();
//モーダルウィンドウをフェードインする
$("#modal-content").fadeIn("slow");
//[#modal-overlay]をクリック
$("#modal-overlay).unbind().click(function() {
//[#modal-content]と[#modal-overlay]をフェードアウト
$("#modal-content,#modal-overlay").fadeOut("slow", function() {
//[#modal-overlay]を削除する
$('#modal-overlay').remove();
});
});
});
//リサイズされたら、センタリングをする関数[centeringModalSyncer()]を実行する
$(window).resize(centeringModalSyncer);
//画面(ウィンドウ)の幅、高さを取得
const w = $(window).width();
const h = $(window).height();
//センタリングを実行する関数
function centeringModalSyncer() {
// モーダルウィンドウ(#modal-content)の幅、高さを取得
const cw = $("#modal-content").outerWidth();
const ch = $("#modal-content").outerHeight();
//センタリングを実行する
$("#modal-content").css({ "left": ((w - cw) / 2) + "px", "top": ((h - ch) / 2) + "px" });
}
});
ボタンを押してモーダルウィンドウを表示し、画面外を押して閉じれば成功です。
Spring Securityの依存性を注入するとアプリケーションを起動した際にSpring Securityのデフォルトのログイン画面が表示されるようになります。
まずは、自前で作成したログイン画面を表示させたいので
適当に作成したHTMLをcontrollerクラスのgetmappingで呼びます。
次に、javaconfigで設定を行います。
設定を行うためのwebsecurityconfigクラスを作成します。このクラスは、websecurityconfigureradapterを継承します。
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.security.config.annotation.web.builders.HttpSecurity;
import org.springframework.security.config.annotation.web.builders.WebSecurity;
import org.springframework.security.config.annotation.web.configuration.EnableWebSecurity;
import org.springframework.security.config.annotation.web.configuration.WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter;
import org.springframework.security.crypto.bcrypt.BCryptPasswordEncoder;
import org.springframework.security.crypto.password.PasswordEncoder;
import org.springframework.security.web.util.matcher.AntPathRequestMatcher;
@Configuration
@EnableWebSecurity
public class WebSecurityConfig extends WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter{
@Override
public void configure(WebSecurity web) throws Exception {
// spring securityで無視するリクエストパスを設定 / **より下の階層は自由にアクセス可能
web.ignoring().antMatchers("/css/**", "/images/**", "/js/**");
}
@Override
protected void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
/*ログインページ
ログインのアクション
認証するときのパラメーター
認証成功時の遷移先
ログアウトのアクション
ログアウト成功時のURL
cookieの削除
セッションを無効にする*/
http.formLogin()
.loginPage("/login/form")
.loginProcessingUrl("/signin")
.usernameParameter("mailaddress")
.passwordParameter("password")
.defaultSuccessUrl("/mypage")
.and()
.logout()
.logoutRequestMatcher(new AntPathRequestMatcher("/signout"))
.logoutSuccessUrl("/login/form")
.deleteCookies("JSESSIONID")
.invalidateHttpSession(true)
.permitAll();
//ログイン前に許可する処理
http.authorizeRequests()
.antMatchers("/user/add").permitAll()
.antMatchers("/login/change/password").permitAll()
.anyRequest().authenticated();
}
@Bean
PasswordEncoder passwordEncoder() {
return new BCryptPasswordEncoder();
}
}
ハッシュ化の方式はbcryptpasswordencoderを用いたいのでbcryptpasswordencoderをjavaconfigでbeanに追加します。 ここまで完了すると自作したログインページが表示されるようになります。
新規ユーザー作成画面からパスワードの入力フォームに入力された文字をcontrollerクラスで取得します。 serviceクラスにパスワードをハッシュ化するメソッドを作成します。
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.security.crypto.password.PasswordEncoder;
@Autowired
PasswordEncoder passwordEncoder;
public void hashPassword(String password) {
passwordEncoder.encode(password);
}
controllerにserviceで作成したメソッド呼び出し取得した文字を引数に渡してハッシュ化させて登録します。
データベースに登録したユーザーのパスワードがハッシュ化されているか確認してください。
userテーブルからユーザーを取得するmapperを書きます。
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<!DOCTYPE mapper PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN" "http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd">
<mapper namespace="com.example.demo.mapper.UserMapper">
<select id="findUser" resultType="com.example.demo.entity.User">
select user_id,user_name,mailaddress,password,admin_flg,isdeleted from m_user where mailaddress = #{mailaddress};
</select>
</mapper>
@Mapper
public interface UserMapper {
public Optional<User>findUser(String mailaddress);
}
ユーザーを照合するクラスを書きます。
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collection;
import org.springframework.security.core.GrantedAuthority;
import org.springframework.security.core.authority.SimpleGrantedAuthority;
import org.springframework.security.core.userdetails.UserDetails;
import lombok.Data;
@Data
public class LoginUserDetailsImpl implements UserDetails{
private User loginUser;
private Collection<GrantedAuthority>authorities;
public LoginUserDetailsImpl(User loginUser) {
this.loginUser = loginUser;
String role = null;
if(loginUser.getAdmin_flg() == 1) {
role = "ADMIN";
}else if(loginUser.getAdmin_flg() == 0) {
role = "USER";
}
this.authorities = new ArrayList<>();
this.authorities.add(new SimpleGrantedAuthority("ROLE_" + role));
}
@Override
public Collection<? extends GrantedAuthority> getAuthorities() {
return authorities;
}
@Override
public String getPassword() {
return loginUser.getPass();
}
@Override
public String getUsername() {
return loginUser.getUser_name();
}
@Override
public boolean isAccountNonExpired() {
return true;
}
@Override
public boolean isAccountNonLocked() {
return true;
}
@Override
public boolean isCredentialsNonExpired() {
return true;
}
@Override
public boolean isEnabled() {
if(loginUser.getIsdeleted() == 1) {
return false;
}
return true;
}
}
ログイン画面から直接URL書き換えて遷移しないようにloginconfigクラスを作成します。
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.config.annotation.ViewControllerRegistry;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.config.annotation.WebMvcConfigurer;
@Configuration
public class LoginConfig implements WebMvcConfigurer{
public void addViewContorllers(ViewControllerRegistry registry) {
registry.addViewController("/login/form").setViewName("/pages/login_form");
}
}
今回はjunit5を使ってテストしました。
調べてみるとjunit4でテストを書いているのを多く見かけるのでリンク参照 junit5のメリット junit5のアノテーション
画面テスト
//コントローラクラスのメソッド
@GetMapping("/home")
public ModelAndView index(ModelAndView mav) {
mav.setViewName("index");
return mav;
}
※コントローラクラスに画面を呼び出すメソッドをString型で作成されているのはよく見かけますが 戻り値が文字列として認識してエラーになります。動作自体は問題ないです。 テストする際はModelAndView?を使ってテストします。
//テストクラスのメソッド
@Test
public void getIndexTest() throws Exception {
mockMvc.perform(get("/home"))
.andExpect(status().isOk())
.andExpect(view().name("index"));
}
ログインとmapperのテスト
package com.example.demo;
import static org.junit.jupiter.api.Assertions.*;
import static org.springframework.test.web.servlet.request.MockMvcRequestBuilders.*;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.test.autoconfigure.web.servlet.AutoConfigureMockMvc;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
import org.springframework.security.core.Authentication;
import org.springframework.security.core.context.SecurityContextHolder;
import org.springframework.security.test.context.support.WithUserDetails;
import org.springframework.test.web.servlet.MockMvc;
import org.springframework.test.web.servlet.MvcResult;
import com.example.demo.mapper.EmployeeMapper;
import com.example.demo.model.Employee;
@SpringBootTest
@AutoConfigureMockMvc
class ApplicationTests {
@Autowired
MockMvc mockMvc;
@Autowired
EmployeeMapper employeeMapper;
// データベースアクセス処理テスト
@Test
public void findOneTest() {
Employee e = new Employee();
e = employeeMapper.findOne("testemail@gmail.com");
assertEquals("testname", e.getName());
}
// 認証テスト
@Test
@WithUserDetails(value = "testemail@gmail.com")
public void certificationTest() throws Exception {
// 認証情報を取得
Authentication auth = SecurityContextHolder
.getContext().getAuthentication();
String message = "class = " + auth.getClass() + "\n" +
"name = " + auth.getName() + "\n" +
"credentials = " + auth.getCredentials() + "\n" +
"authorities = " + auth.getAuthorities() + "\n" +
"principal = " + auth.getPrincipal() + "\n" +
"details = " + auth.getDetails();
// 今回は確認のために標準出力しているだけ(ここまで本来は不要らしいです。)
System.out.println(message);
// モックを使用してテスト対象のURL(ログイン成功画面)にアクセスする
MvcResult mvcResult = mockMvc.perform(get("/home/view")).andReturn();
// ユーザ認証許可する設定のためアクセス可能であることを確認
assertEquals("homepage", mvcResult.getModelAndView().getViewName());
}
}